- Iso 7498 2 Security Model 60
- Iso 7498-2 Security Model
- Iso 7498 2 Security Model Diagram
- Iso 7498 2 Security Model Rs
- ISO 7498-2:1989 Information processing systems — Open Systems Interconnection — Basic Reference Model — Part 2: Security Architecture 90.93: ISO/IEC JTC 1: ISO 7498-3:1989 Information processing systems — Open Systems Interconnection — Basic Reference Model — Part 3: Naming and addressing 95.99: ISO/IEC JTC 1.
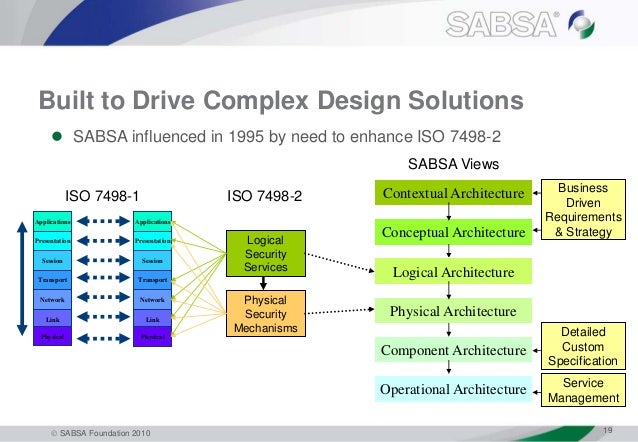
- The OSI reference model for networking (ISO 7498-1) is designed around seven layers arranged in a stack. The OSI security architecture reference model (ISO 7498-2) is also designed around seven layers, reflecting a high level view of the different requirements within network security.
Buy iso 7498-2: 1989 information processing systems - open systems interconnection - basic reference model - part 2: security architecture from sai global Skip to content Close. For other uses, see. Security service is a service, provided by a layer of communicating open systems, which ensures adequate security of the systems or of data. The OSI security architecture reference model (ISO 7498-2) is also designed around seven layers, reflecting a high level view of the different requirements within network security. In OSI model each layer has its own functionality and according to that it has different security features as listed below.
For the purposes of this Standard the following definitions apply.
3.1 Reference Model Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in [ISO 7498-1]:
See [ISO 7498-1].
See [ISO 7498-1].
See [ISO 7498-1].
3.2 Reference Model Security Architecture Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in [ISO 7498-2]:
See [ISO 7498-2].
Note
The definition is 'the property that information is not made available or disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities or processes.'
See [ISO 7498-2].
Note
The definition is 'the corroboration that the source of data received is as claimed.'
See [ISO 7498-2].
Note
The definition is 'the property that data has not been altered or destroyed in an unauthorized manner.'
See [ISO 7498-2].
Note
The definition is 'the generation, storage, distribution, deletion, archiving and application of keys in accordance with a security policy.'
See [ISO 7498-2].
Iso 7498 2 Security Model 60
Note
The definition is 'Data appended to, or a cryptographic transformation of, a data unit that allows a recipient of the data unit to prove the source and integrity of that unit and protect against forgery e.g., by the recipient.'
3.3 ACSE Service Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in [ISO 8649]:
See [ISO 8649].
3.4 Security Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in [ECMA 235]:
Iso 7498-2 Security Model
See [ECMA 235].
Note
The definition is 'security information that represents, or will represent a Security Association to an initiator or acceptor that has formed, or is attempting to form such an association.'
3.5 DICOM Introduction and Overview Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.1:
Attribute.
Service-Object Pair Class (SOP Class).
3.6 DICOM Conformance Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.2:
Security Profile.
3.7 DICOM Information Object Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.3:
Module.
3.8 DICOM Service Class Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.4:
Service Class.
Service-Object Pair Instance (SOP Instance).
3.9 DICOM Communication Support Definitions
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.8:
DICOM Upper Layer Service.
3.10 DICOM Security Profile Definitions
The following definitions are commonly used in this Part of the DICOM Standard:
A Transport Connection that provides some level of protection against tampering, eavesdropping, masquerading.
A digest or hash code derived from a subset of Data Elements.
An electronic document that identifies a party and that party's public encryption algorithm, parameters, and key. The Certificate also includes, among other things, the identity and a digital signature from the entity that created the certificate. The content and format of a Certificate are defined by ITU-T Recommendation X.509.
3.11 DICOM Data Structures and Encoding
Iso 7498 2 Security Model Diagram
This Part of the Standard makes use of the following terms defined in PS3.5:
Iso 7498 2 Security Model Rs
Data Set.

Comments are closed.