- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Pdf
- Chain Analysisdialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
- Chain Analysisdialectical Behavioral Training Relias
Here are ten American fast food restaurant chains operating in the Netherlands. Many are well-established, while others are just beginning their roll out into the Dutch marketplace…
McDONALD’S – The first McDonald’s Netherlands location opened in 1971 in the city of Zaandam (North Holland). The company struggled in the early years, not fully recognizing certain key behavioral differences in the Dutch, such as the large percentage that cycle to work or to the train station. Those were potential customers that weren’t visiting the restaurants which had been located along highways. But once the locations were moved to city centers, the brand began to flourish. Today there are approximately 250 McDonald’s locations across the Netherlands, including 17 in Amsterdam, 15 in Rotterdam, 8 in The Hague and 5 in Utrecht.
KFC – The first Kentucky Fried Chicken location in Holland opened in 1972 in Rotterdam. Today there are over 55 KFC locations in the Netherlands with a third of them (18) in South Holland. Yum Brands (parent company of KFC) recently sold many Dutch KFC locations to Collins Foods, the largest Australian KFC franchisee. Collins Foods plans to open an additional 20 locations in the Netherlands by 2021. You can get delivered to your home through Thuisbezorgd.
BURGER KING – The first Burger King Netherlands restaurant opened in 1981. It has since grown to more than 60 locations across the country including Amsterdam (8), Rotterdam (3), The Hague (2), Eindhoven (2), Arnhem (2), Delft (2), Groningen (2), Amersfoort (2) and Utrecht (2). Burger King also offers home delivery for customers in the Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Groningen, Schiedam and Hoofddorp areas through Thuisbezorgd.
SUBWAY – The first Subway Netherlands location was opened in Eindhoven in 2000. The brand has expanded quickly via a network of franchisee-owned locations. Today there are 180 Subway locations across the country including Amsterdam (12), The Hague (12), Rotterdam (10) and Utrecht (5). You can have Subway delivered to your home through Thuisbezorgd.
DOMINO’S – In 2001, Domino’s Pizza set up a ‘regional resource center’ here in the Netherlands (the first outside the United States) after taking a majority share in the Dutch license holder. That move would later be key in the brand’s European expansion. Domino’s is the market leader in home pizza delivery in Holland with approximately 50 locations (13 in Amsterdam alone).
STARBUCKS – In 2007, the first Starbucks in the Netherlands opened at Schiphol Airport and was operated by licensee HMS Host. Two years later, the first Starbucks train station location was opened at Leiden Centraal (operated by licensee Servex, a subsidiary of NS). In 2011, the first inner city Starbucks opened on Leidsestraat in Amsterdam. Today there are approximately 50 Starbucks points-of-sale throughout the country including 15 in Amsterdam and 5 each in The Hague and Rotterdam.
DUNKIN’ DONUTS – The popular American donut brand wasn’t so popular during its first attempt at entering the Dutch market in the late 1990s. After nearly two decades away from the Netherlands, the company re-entered the market in 2017, starting with 4 locations in Amsterdam. Since then it has expanded with 4 additional shops in Amsterdam, plus locations in Amstelveen (1), Almere (1), Eindhoven (1), Hilversum (1), Leiden (1), Roermond (1), Rotterdam (2), Tilburg (1) and Utrecht (3). The newest Dunkin’ Donuts Netherlands shop is on Spui in The Hague city center. You can have Dunkin Donuts delivered to your home through Thuisbezorgd.
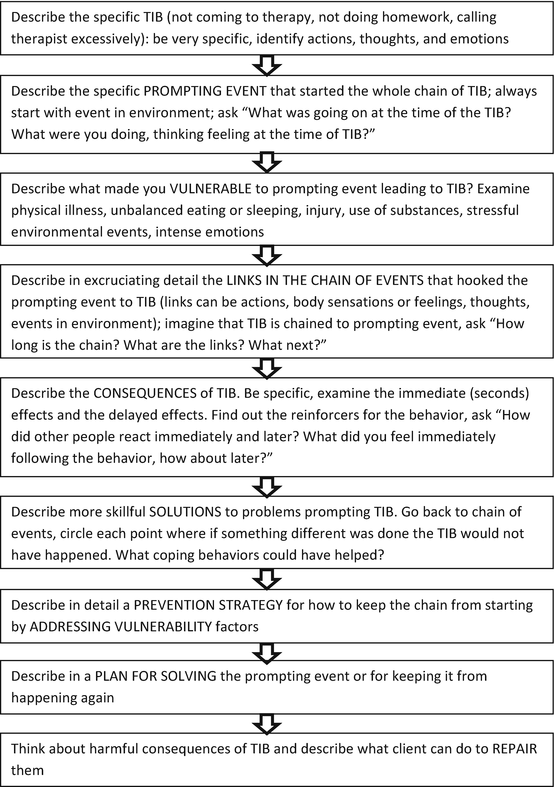
Behavioral chain analyses, which are common in behavioral and cognitive-behavioral treatments more broadly, are the primary assessment tool in Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT). As such, they are conducted in nearly every DBT session. What is “Chaining” in Applied Behavior Analysis? Applied Behavior Analysis is a popular therapy method used with individuals with autism and related conditions, those interested in the field often inquire what is “chaining” in ABA? Chaining is a method that therapists use to help children gain proficiency in complex, multi-step directions.

Chaining Chaining refers to a method of teaching a behavior using behavior chains. Behavior chains are sequences of individual behaviors that when linked together form a terminal behavior. When teaching a behavior using chaining, the first step is to complete a task analysis. One of my favorite tools for helping others discover places where small simple changes can be applied to a sequence of events that ultimately ends in the out.
FIVE GUYS – The Five Guys American burger chain has jumped across the pond, landing in the Netherlands in 2017. It currently operates 9 locations – Almere, Eindhoven, Rotterdam (2), The Hague (2), Tilburg and Utrecht (2) with another to come in Scheveningen. The company has been in a fight with the city of Amsterdam, which has blocked Five Guys from opening locations in the city as part of the municipality’s desire to reduce the number of fast food restaurants. You can get Five Guys delivered to your home through Thuisbezorgd.
PAPA JOHN’S – This well-known American pizza chain crossed the Atlantic in 2016 and has grown quickly ever since. At last count they were up to 26 locations including in Amstelveen, Amsterdam, Delft, Eindhoven, Gouda, Groningen, Haarlem, The Hague, Hilversum, Leiden, Rotterdam, Utrecht and Zoetermeer. You can order Papa John’s pizza with home delivery or takeaway.
TACO BELL – The American Mexican-themed fast food restaurant chain, Taco Bell, has had a small presence in the Netherlands since 2017 with 3 locations in the south of the country (Breda, Eindhoven and Tilburg). A fourth was added recently in Amersfoort. Whether the Yum brand can grow substantially is still to be seen. For fans of Taco Bell living in one of the cities listed, it is possible to order through Thuisbezorgd and have it delivered to your home.
NOTE: According to the Dutch national statistics bureau, CBS, the fast food category recently showed the highest growth rate in the food and beverage sector in the Netherlands.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Pdf
Related information…
Training often requires that a sequence of arbitrary behaviors be structured so that they occur in a specific order. This order of occurrence is based on a predetermined continuity in which one behavior must always precede the next in a set sequence. Orderly sequencing is accomplished by making the advancement of the series contingent on the emission of a predetermined response occurring before the next one in the series is selected. To accomplish this goal, each task in the chain is brought under the stimulus control of a dual-functioning signal serving both to reinforce the correct antecedent behavior conditionally and to simultaneously select the next response in the series. This pattern is repeated until the entire sequence of behaviors is emitted and terminally reinforced.

Within the chain, each discriminative stimulus (Sd) provides conditional reinforcement for the behavior that it follows and simultaneously selects the next response. The SD's dual function is an outcome of the way in which a chain is constructed. The chain is built up by connecting the final response with the terminal reinforcer and then adding on successive behaviors up to the origin of the chain. To obtain reinforcement, dogs must perform each response in the chain at the proper time. Each Sd in the chain not only selects the next behavior in the chain but also reinforces the preceding behavior because it advances the dog one step closer to the terminal reinforcer (Sr+).

perhaps the easiest way to show how chaining works is to use a common example. The recall pattern involves a six-part chain: sit, stay, come, sit-front, finish, and sit. Both the terminal response and the origin are sit responses. Between the origin and the terminal response are four chained responses: stay, come, sit-front, and finish. These various components are linked through shared stimulus control and conditioned reinforcement. The chain is terminated with a sit response and final reinforcement at the trainer's left side. The terminal response is under the stimulus control of the Sd 'Sit.' 'Sit' not only selects the terminal response, it also conditionally reinforces the preceding finish behavior. The next link is the finish behavior, which is brought under the stimulus control of the Sd 'Heel.' 'Heel' not only selects the behavior of moving to the trainer's side but also conditionally reinforces the previous link in the chain—sit-front. Sit-front is under the stimulus control of the Sd 'Sit,' which not only selects the sit response but also conditionally reinforces coming. Coming is under the stimulus control of the Sd 'Come,' which also conditionally reinforces the dog for staying. The Sd 'Stay' selects staying behavior and conditionally reinforces the sit response. The sit response is the origin of the chain and is under the stimulus control of the SD 'Sit'

A far more common form of chaining in everyday dog training is called forward chaining. Although forward chaining lacks the behavioral elegance of backward chaining, it does offer many valuable features and several distinct advantages. Forward chaining requires only that a series of responses be performed on cue for a single reward. The forward chain is built up by placing each response component on an intermittent schedule of reinforcement and randomizing its occurrence in the chain sequence. Such a strategy of intermittent reinforcement and randomization results in the development of a hoped-for expectancy occurring equally with each link in the chain—a result that usually translates into a general strengthening of the chain, as well as immunizing component responses against extinction. It should be noted in the case of backward chaining that behaviors near the end of the chain are the most strongly reinforced, since they are the closest to the terminal reinforcer. In the case of forward chaining, responses near the origin of the chain are the strongest with the lure of reinforcement rapidly declining as the chain of responses is extended. Care must be taken, therefore, not to extend the forward chain too rapidly, perhaps causing a dog to quit. An important advantage of forward chaining is that it provides a means to place acquired behavior on an intermittent schedule. For example, instead of reinforcing a dog on every occasion for sitting, forward chaining might require the dog to perform any combination of the series stand, sit, down, sit from the down, and sit-stay for a single re ward. Individual responses comprising the foregoing chain are conditionally reinforced at each step with praise ('Good'), but the final reward is presented only after the required sequence is performed or the whole series is completed successfully. Forward chaining teaches dogs to expect reinforcement after a certain amount of work, regardless of the actual behaviors performed. Also, the order of responses can be easily altered without significantly affecting the viability of the chain. The response order of a backward chain is locked in without much room for variability or change, other than shortening the chain by assigning the origin to a response closer to the terminal reinforcer. Also, if any of the behaviors in the backward chain fail (a highly likely outcome with responses near the origin of a long chain), the whole chain breaks down. Although carefully constructed backward chains can be immunized against extinction, the sheer complexity of the chain and the repeated occurrence of individual component responses without direct reinforcement make backward chains very sensitive to breakdown under natural training conditions.
Chain Analysisdialectical Behavioral Training Techniques
Continue reading here: Rehearsal and Staging
Chain Analysisdialectical Behavioral Training Relias
Was this article helpful?

Comments are closed.